
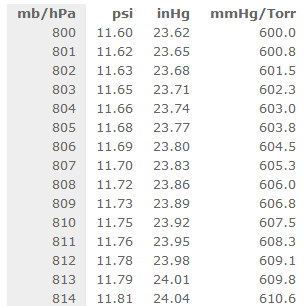
Convert mmHg to SI units as follows: 1 mmHg = 0.13332 kPa. The normal adult blood pressure is less than 120 mmHg systolic BP (SBP) and less than 80 mmHg diastolic BP (DBP). In medicine, blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg, very close to one Torr).

The airtightness of buildings is measured at 50 Pa. For sound in air, a pressure of 20 μPa is considered to be at the threshold of hearing for humans and is a common reference pressure, so that its SPL is zero. Loudness is the subjective experience of sound pressure and is measured as a sound pressure level (SPL) on a logarithmic scale of the sound pressure relative to some reference pressure. The pascal is used to measure sound pressure. This applies not only to the thermodynamics of pressurised gases, but also to the energy density of electric, magnetic, and gravitational fields. The pascal is also equivalent to the SI unit of energy density, the joule per cubic metre. In engineering the megapascal (MPa) is the preferred unit for these uses, because the pascal represents a very small quantity.Īpproximate Young's modulus for common substances Material In materials science and engineering, the pascal measures the stiffness, tensile strength and compressive strength of materials. Medical elastography measures tissue stiffness non-invasively with ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging, and often displays the Young's modulus or shear modulus of tissue in kilopascals. Geophysicists use the gigapascal (GPa) in measuring or calculating tectonic stresses and pressures within the Earth. The pascal (Pa) or kilopascal (kPa) as a unit of pressure measurement is widely used throughout the world and has largely replaced the pounds per square inch (psi) unit, except in some countries that still use the imperial measurement system or the US customary system, including the United States. Unicode has dedicated code-points U+33A9 ㎩ SQUARE PA and U+33AA ㎪ SQUARE KPA in the CJK Compatibility block, but these exist only for backward-compatibility with some older ideographic character-sets and are therefore deprecated. In contrast, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends the use of 100 kPa as a standard pressure when reporting the properties of substances.
#5 pa to psi iso#
This value is often used as a reference pressure and specified as such in some national and international standards, such as the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 2787 (pneumatic tools and compressors), ISO 2533 (aerospace) and ISO 5024 (petroleum). The unit of measurement called an atmosphere or a standard atmosphere (atm) is 101 325 Pa (101.325 kPa). One pascal is the pressure exerted by a force of magnitude one newton perpendicularly upon an area of one square metre.
Where N is the newton, m is the metre, kg is the kilogram, s is the second, and J is the joule. The pascal can be expressed using SI derived units, or alternatively solely SI base units, as:ġ P a = 1 N m 2 = 1 k g m ⋅ s 2 = 1 J m 3 The name pascal was adopted for the SI unit newton per square metre (N/m 2) by the 14th General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1971. The unit is named after Blaise Pascal, noted for his contributions to hydrodynamics and hydrostatics, and experiments with a barometer. In Canada these reports are given in kilopascals. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals).

Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. The unit of measurement called standard atmosphere (atm) is defined as 101,325 Pa. It is also equivalent to 10 barye (10 Ba) in the CGS system.Ĭommon multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is a SI coherent derived unit defined as one newton per square metre (N/m 2). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). A pressure gauge reading in psi (red scale) and kPa (black scale)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
